#10 Fighting The Semantic Gap On CBIR Systems
CBIR which stands for Content Based Image Retrieval is
a technique that involves querying an image. Which you then retrieve matches to the queried
image based on its similarity results. It typically involves comparing the low-level
features of an image, including color, texture, and shape. However, what if you
want to compare high level features? High level features mean, the semantic
meaning behind an image that humans are basically able to discern. For example,
say you want, a tall happy person, or a happy small dog. A person would be able
to pick out images pretty easily from a set that match these criteria, a system
not so much. What exactly can be done to bridge this Semantic Gap?
The academic article “Fighting the Semantic Gap on CBIR Systems through New Relevance Feedback Techniques” mentions using relevance feedback techniques to combat this.” The paper describes the process as “Therefore, by gathering the users´ indications, algorithms can be developed to change the placement of the query, or to change the similarity function employed in order to better comply to the users’ expectations. The approach that asks to the user to set the relevance of the images to a given query and to reprocess it based on the users´ feedback is called relevance feedback (RF) and is been proven to be quite effective in bridging the semantic gap.”[1] Two new Relevance Feedback Techniques are introduced called, Relevance Feedback Projection and Multiple Point Projection.
Relevance Feedback Projection which is described in the paper as “The proposed Relevance Feedback Projection technique analyzes each feature (attribute) from the feature vector separately, classifying them into a “relevance rule”, indicating the relevant and irrelevant objects. The values of the attribute being processed (relevant images) are placed in the relevant interval”.[1] So the features from an image are analyzed separately instead of together this causes the accuracy of it to increase compared to regular Relevance Feedback. Irrelevant images are of course pushed out in order to make more room for relevant images.
Of course, to increase the accuracy even further you
have to improve upon precision. Precision being the fraction of relevant
images. To increase the precision, it is beneficial to combine the previous
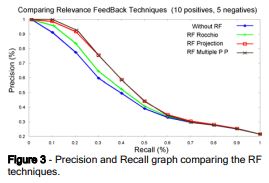
technique with Multiple Point Projection. The figure below outlines how Multiple
Point Projection compares to other techniques. The paper explains that in the
figure “Our proposed techniques achieve a precision of 98% for 0.1 of
recall and 88% when the recall is 20% when applying the RF Projection
technique, and 100% and 89% respectively for the Multiple Point Projection.”[1]
The techniques had a pretty good precision but combining them together can be
beneficial.
The proposed techniques seem promising when trying to bridge the semantic gap. A good solution to understanding high level features, is introducing a human element to it. How you go about it is important, Relevance Feedback Projection seems like a good technique to use for modern systems. However, it seems the best method in utilizing these techniques is to combine both Relevance Feed Projection and Multiple Point Projection.
References
[1] A. J. M. Traina, J. Marques and C. Traina,
"Fighting the Semantic Gap on CBIR Systems through New Relevance Feedback
Techniques," 19th IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems
(CBMS'06), 2006, pp. 881-886, doi: 10.1109/CBMS.2006.88.


Bao,
ReplyDeleteVery interesting topic and well written summary.